Quiz - Medicines
1. Put the following statements about developing new medicines in the correct order. Drag and drop the statements where you think they should go:
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- Safety tests in animals start
- Research to understand the disease
- Clinical trials in patients start
- Human volunteers given the new medicine
- In vitro testing using cell cultures, tissue cultures and whole organs
- Application submitted to market the medicine
2. An agar plate has been pre-innoculated with bacteria grown from a swab taken from an infected wound. Discs containing four different antibiotics are carefully placed on the surface of the agar. The dish is then incubated at 25°C. After one week the plate looks like this:
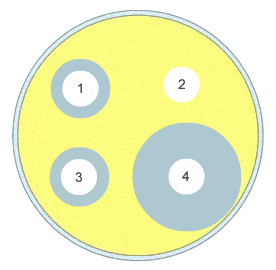
1.
Which antibiotic should be used to treat the infection?
2.
After 3 days treatment the wound is healing well so the patient decides not to take the remaining doses of antibiotic.
Two days later the wound is worse so he re-starts taking the antibiotic, but it doesn’t cure the infection. Why not?
3. Select the correct answer from the multi-choices. When you have answered all 4 questions you may check your answers by clicking the button below.
1.
When you culture bacteria in the school lab they are incubated at a temperature of
2.
A chemical which can be used to destroy bacteria inside the body is
3.
Which of the following is NOT a way of avoiding the development of antibiotic resistant bacteria?
4.
Approximately how many years does it take to develop a new medicine?
5.
At which stage of clinical trials is the new medicine first tested to see if it works to treat the disease?
6.
What is a double blind trial?